Quantification of Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Properties of Materials
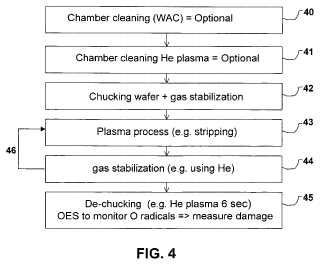
A non-destructive and simple analytical method is provided which allows in situ monitoring of plasma damage during the plasma processing such as resist stripping. If a low-k film is damaged during plasma processing, one of the reaction products is water, which is remained adsorbed onto the low-k film (into pores), if the temperature is lower than 100-150 C. A plasma (e.g. He) that emits high energy EUV photons (E>20 eV) which is able to destruct water molecules forming electronically excited oxygen atoms is used to detect the adsorbed water. The excited oxygen is detected from optical emission at 777 nm. Therefore, the higher the adsorbed water concentration (higher damage), a more intensive (oxygen) signal is detected. Therefore, intensity of oxygen signal is a measure of plasma damage in the previous strip step. The proposed analytical method can be performed in-situ immediately after plasma processing and most preferred the optical emission of oxygen radicals is monitored during the de-chucking step in the plasma chamber.Attached files:
Patents:
US 20,090,068,768
Inventor(s): URBANOWICZ ADAM MICHAL [PL]; BAKLANOV MIKHAIL [BE]
Type of Offer: Sale
« More Physics Patents
