Photoacoustic Detection of Analytes in Solid Tissue and Detection System
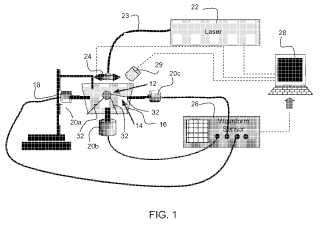
A preferred system for detecting an analyte in solid tissue (12), such as an intact lymph node, in vitro includes a laser (22) arranged to generate a pulsed laser beam into solid tissue, which can be a fully intact lymph node. An acoustic sensor, and preferably at least three acoustic sensors (20a, 20b, 20c) are arranged in different positions to span a three dimensional space, such as in an X, Y and Z coordinate system, to detect photoacoustic signals generated within the lymph node. At least one computer (28) receives signals from the acoustic sensor(s). The computer determines the presence or absence of, and preferably the position of analyte, from the signals and the timing of the signals. A preferred method for detecting an analyte in a lymph node in vitro includes exposing an extracted lymph node to a pulsed laser beam. A photoacoustic signal is sensed.; The photoacoustic signal is analyzed to confirm the presence or absence of an analyte in the lymph node. Preferably, multiple photoacoustic signals are sensed from sensors that span a three dimensional space and the position of analyte is also determined.Attached files:
Patents:
WO 2,010,123,883
Inventor(s): VIATOR JOHN A [US]; DALE PAUL S [US]; MCCORMACK DEVIN [US]
Type of Offer: Licensing
« More Biomedical Patents
« More Acoustical Patents
